DECREASE BODY FAT LEVELS
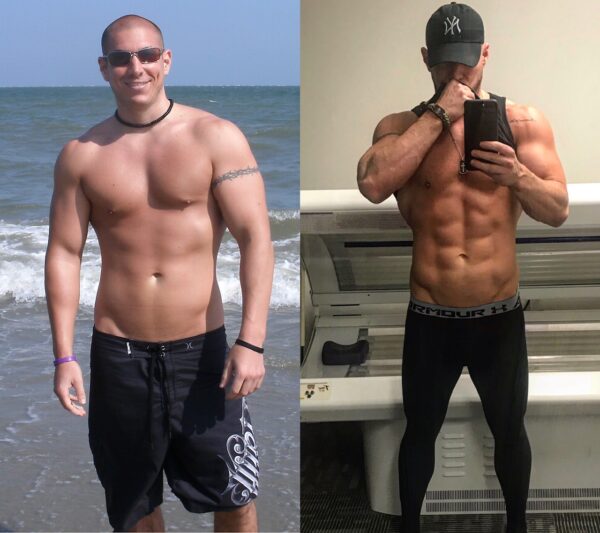
To lose body fat specifically, as opposed to just overall weight loss, requires a targeted approach. To focus on reducing body fat, it’s essential to prioritize strength training to build and maintain muscle mass. This is crucial because muscle tissue is metabolically active and aids in burning calories even at rest. Secondly, consider incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or other metabolism boosting exercises to maximize fat loss.
IMPROVE BODY COMPOSITION
Improving your overall body composition is what creates a lean, toned appearance. If you purely focus on weight loss you will lose a combination of fat and muscle. Creating a smaller version of yourself, but seeing no significant improvements in definition or leanness. If you focus on specifically losing fat while also building muscle, you will purely lose body fat. Creating that lean, toned, athletic look you are going for.
STRENGTH TRAINING IS KEY TO LOSING BODY FAT
Strength training and muscle growth play a crucial role in losing body fat and maintaining a lean physique for several reasons. Firstly, strength training helps increase your muscle mass. When you engage in resistance exercises like weightlifting, your muscle fibers are broken down. As they repair over the next 48-72 hours, the fibers grow back denser and larger than before. Therefore creating additional mass. The repair process itself increases your metabolic rate as the body needs additional calories to repair the damaged tissue. As for keeping fat off long term, muscle mass is more metabolically active than fat. In other words, every pound of muscle causes your body to burn more calories at rest, turbo charging your overall metabolism.
Additionally, strength training helps preserve lean muscle mass while you are in a calorie deficit. When you aim to lose body fat, you typically reduce your calorie intake, which can cause your body to burn both fat and muscle for energy. However, by incorporating strength training into your routine, you signal to your body to continue preserving and growing muscle mass. This eliminates any muscle loss from your cutting program and ensures the weight you lose comes purely from fat stores.
Moreover, building muscle through strength training can lead to an improved body composition. As you increase your muscle mass, your body becomes more toned and defined, giving you a leaner appearance. This is particularly important for those aiming for a well-defined physique.
Furthermore, strength training has a positive impact on your overall health. It helps improve bone density, joint stability, and posture. It also enhances your physical performance and reduces the risk of injury.
WHAT IS HIIT TRAINING
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) cardio is often considered superior to traditional steady state cardio, and it is a staple of GPT training sessions. One of the key reasons HIIT is highly regarded is its efficiency. HIIT workouts typically involve short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. This type of training allows you to burn more calories in a shorter amount of time compared to steady state cardio. The intense intervals push your body to work at its maximum capacity, maximizing calorie burn and boosting your metabolism even after the workout is over. So, if you’re looking for a time-effective way to improve cardiovascular fitness and lose body fat, HIIT is a great option.
HIIT TRAINING FOR FAT LOSS
Another benefit of HIIT is its ability to improve your cardiovascular endurance. By alternating between high-intensity intervals and lower-intensity recovery periods, HIIT challenges your heart and lungs to adapt quickly. Over time, this can lead to improved oxygen utilization, increased aerobic capacity, and better overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, HIIT has been found to be effective at reducing body fat, especially stubborn belly fat. The intense intervals in HIIT workouts stimulate the release of growth hormones, which can promote fat burning and muscle building simultaneously. This can result in a leaner physique and improved muscle definition.
Moreover, HIIT workouts offer variety and can be tailored to different fitness levels and preferences. You can choose from a wide range of exercises such as running, cycling, bodyweight exercises, or even dancing. This variability helps prevent boredom, making it easier to stick with your exercise routine in the long term.





DIET & NUTRITION TO LOSE BODY FAT
You can’t outwork a bad diet. At GPT, we design custom meal plans to ensure our clients stay within their caloric and macronutrient guidelines. By doing so, we can take a scientific, data-based approach to weight loss. Most people we encounter have no idea whatsoever how many calories, or how many carbohydrate grams they consume daily. We can’t determine how many calories to burn if we don’t know what your intake is. It’s also difficult to determine how much to decrease your food intake since we don’t know where we’re starting.
We also encourage our clients to utilize the thermogenic properties of food by eating as frequently as possible. Our meal plans allow clients to eat 6-8 times per day while staying within their caloric and macronutrient guidelines. Every time you consume food your body must convert that food into energy, which gives a jolt to your metabolism. We can manipulate this into additional fat loss by eating controlled portions every 2-3 hours and keeping our metabolism peaked all day.
INTERMITTENT FASTING
Intermittent fasting is a dietary approach that involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating. It typically involves dividing the day or week into specific time windows for eating and fasting. During the fasting period, the body undergoes a series of metabolic changes that can promote fat burning and cellular repair. By limiting the time window for eating, intermittent fasting can help control calorie intake and potentially lead to weight loss. Additionally, studies suggest that it may have various health benefits, such as improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, and enhanced brain function.